Addressing Treatment Challenges in Multi-Resistant Patients With Psoriasis: Promising Results With IL-23 Inhibitor

This letter to the editor addresses the treatment challenges for psoriasis patients resistant to multiple biological therapies, proposing categorizing those failing to respond to at least four biologics as multi-resistant. Based on their experience with 10 such patients at the Dermatologic Clinic of the University of Turin, the authors note significant improvement with the IL-23 inhibitor risankizumab. Three out of six patients achieved a 100% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score at 16 weeks, despite comorbidities and difficult-to-treat psoriasis variants.
Dietary Adjustments: Exploring the Potential of the Mediterranean Diet in Alleviating Psoriasis Severity

Despite advancements in medical treatments, the role of lifestyle factors, particularly dietary adjustments, remains relatively unexplored in the treatment of Psoriasis. Many individuals have turned to dietary modifications, with the Mediterranean diet (MeD) gaining attention for its anti-inflammatory properties. Studies suggest that adhering to the MeD may alleviate psoriasis severity, potentially through its modulation of the gut microbiome.
Psoriasis Biologic Treatment Linked to Higher Demodex Density

A recent cross-sectional study explored the correlation between psoriasis treatment using biologics and Demodex mite density. The study, conducted from May to June 2023, compared Demodex mite density in patients with psoriasis undergoing biologic treatment with those receiving no treatment or topical therapy. Utilizing the skin surface biopsy technique, the researchers observed significantly higher Demodex mite density and prevalence of demodicosis among patients treated with biologics, particularly evident on the cheeks and forehead.
Danish Study Links Psoriasis to Increased Risk of Diabetes Mellitus: Insights into Complex Interplay

Psoriasis, a skin condition, has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular events and cardiovascular risk factors, alongside the potential association with diabetes mellitus (DM). However, conflicting findings exist regarding this connection, and nationwide data on the risk of new-onset DM in patients with psoriasis are lacking. To address this gap, a Danish study tracked over 4.6 million individuals for up to 13 years, identifying 52,613 patients with psoriasis, including 6,784 with severe psoriasis. The study found that the incidence rates of new-onset DM were elevated in patients with psoriasis compared to the reference population, with higher rates observed in those with severe psoriasis.
Exploring Biosimilars: Manufacturing, Regulation, and Future Prospects

The review offers a detailed examination of biosimilars, akin to biologics but more affordable, elucidating their intricate manufacturing and regulatory approval processes. It also delves into the distinctions between biologics, biosimilars, and generics, highlighting the complexities of biosimilar development and the necessity for stringent quality control. Additionally, it provides a comprehensive roster of EMA-approved biosimilar medicines for dermatological conditions, emphasizing their cost-saving potential and enhanced accessibility to advanced healthcare.
Unveiling Follicular Psoriasis: Case Study Sheds Light on Rare Variant in Brazilian Patient

This letter to the editor highlights follicular psoriasis (FP), a rare variant of psoriasis, with a particular focus on its manifestation in a 58-year-old diabetic woman in Brazil. The patient presented with erythematous, keratotic, exclusively follicular papules, initially misdiagnosed as other dermatological conditions. Despite therapeutic attempts with antibiotics, the condition persisted until a correct diagnosis was reached via histopathological examination, confirming FP. Treatment with acitretin resulted in improvement after two months. The letter emphasizes the importance of recognizing this variant, particularly in populations with higher melanin levels, where follicular involvement in psoriasis might be overlooked.
Meta-Analysis Finds Elevated Adipokine and Cytokine Levels in Patients With Psoriasis, Identifies Potential Biomarkers

A meta-analysis of 63 studies involving 2,876 psoriasis patients and 2,237 healthy controls investigated the association of serum levels of adipokines and cytokines with psoriasis. The study found that serum levels of several markers, including TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-18, IL-22, chemerin, lipocalin-2, resistin, sE-selectin, fibrinogen, and complement 3, were elevated in patients with psoriasis compared with healthy controls, while adiponectin levels were lower. Additionally, increased serum levels of IL-17 correlated with psoriasis in men, although no significant differences were found for other markers like IL-1β, IL-4, IL-10, IL-12, IL-21, IL-23, visfatin, and omentin.
Psoriatic Arthritis and Metabolic Syndrome: The Interconnected Impact on Health and Cardiovascular Risk

Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is an inflammatory disorder characterized by diverse phenotypes extending beyond the joints, often linked with metabolic syndrome (MetS). MetS, marked by obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia, has a higher prevalence in patients with PsA, likely due to persistent inflammation and elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines. The coexistence of PsA and MetS significantly elevates the risk of cardiovascular disease, impacting morbidity and mortality. Given this strong association, it’s crucial for healthcare providers to screen patients with PsA for MetS and manage their cardiometabolic risk factors, while also monitoring potential treatment-related adverse effects.
Spesolimab Shows Promise in Treating Rare Skin Disease Generalized Pustular Psoriasis, But Raises Safety Concerns
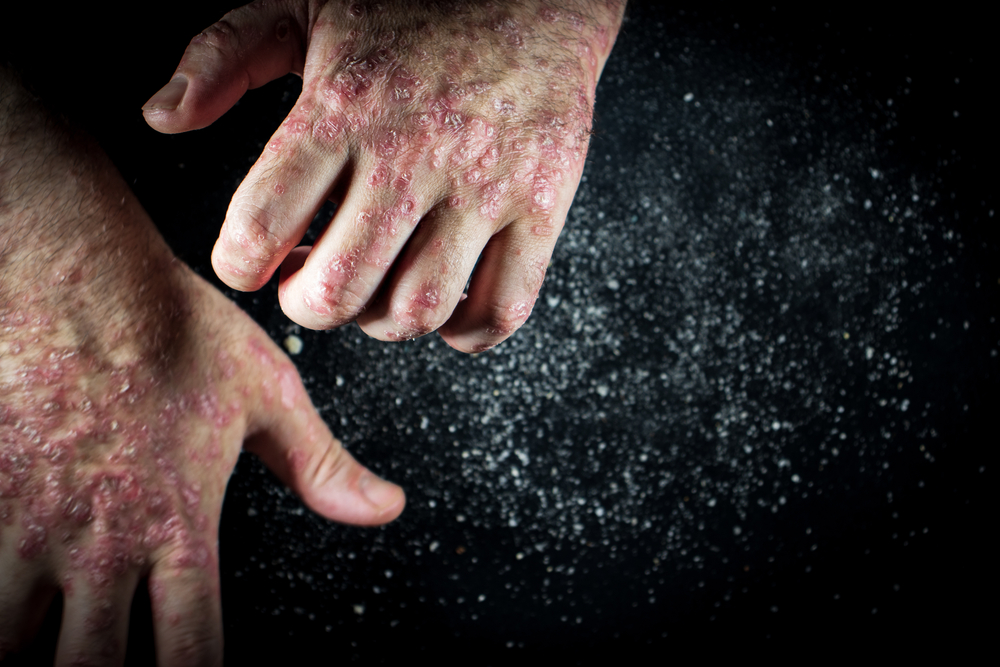
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare and potentially life-threatening inflammatory skin disease characterized by widespread pustules, with interleukin-36 signaling playing a key role in its pathogenesis. The phase 2 trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of spesolimab, an anti-interleukin-36 receptor monoclonal antibody, for treating GPP flares. In this trial, 53 patients experiencing a GPP flare were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive a single 900-mg intravenous dose of spesolimab or placebo. The primary endpoint was a Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPGA) pustulation subscore of 0 at the end of week 1, while the key secondary endpoint was a GPPGA total score of 0 or 1 at the same time point.
For Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Evidence-Based Vaccine Recommendations for Systemic Therapies
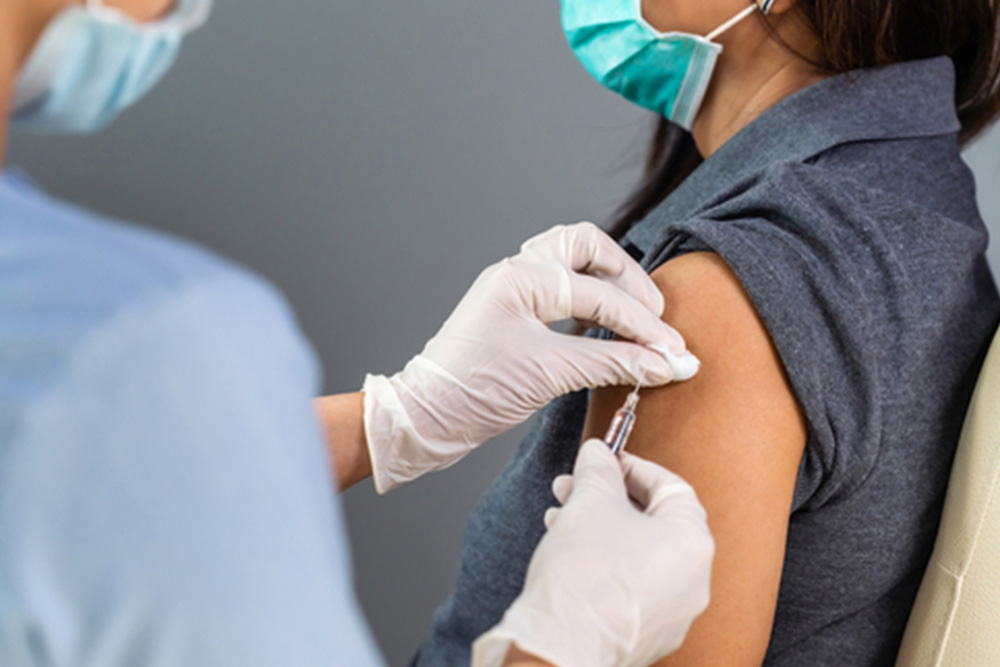
For patients with psoriatic arthritis receiving nonlive or live vaccines, evidence-based recommendations are crucial to determine whether systemic therapies for psoriasis and/or psoriatic arthritis should be paused or continued. The National Psoriasis Foundation Medical Board and COVID-19 Task Force, along with infectious disease experts, developed 22 consensus statements using a modified Delphi process to address vaccine efficacy and safety in this context.

